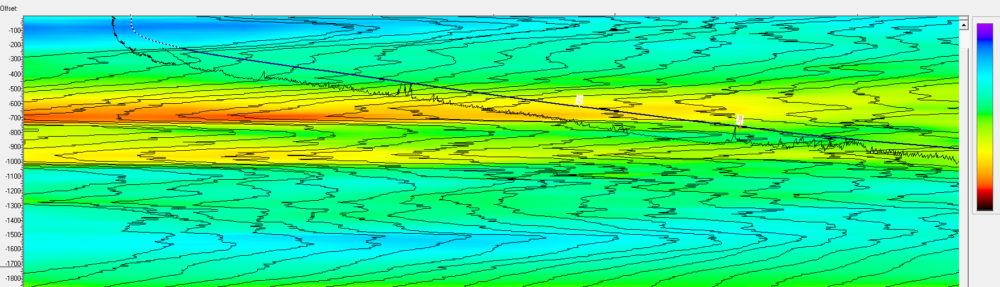
Mathematical models
Three thin layers model
Model consists of three thin layers. The velocity is 3 km/s in the media and 4 km/s in the layers.
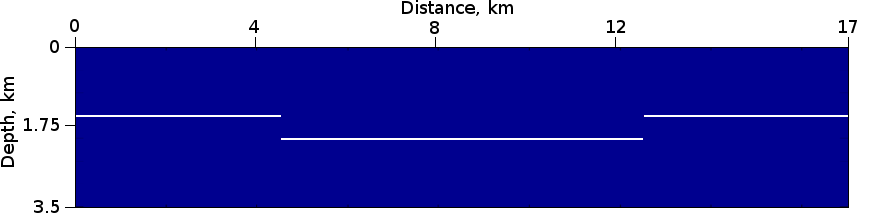
Figure 1: Three thin layers model
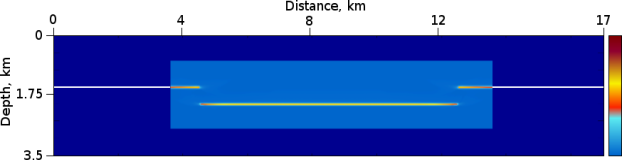
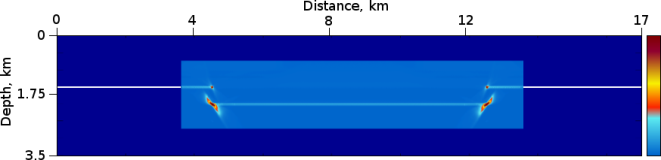
Figure 2: RTH Depth Migration Reflection (a) and Diffraction(b).
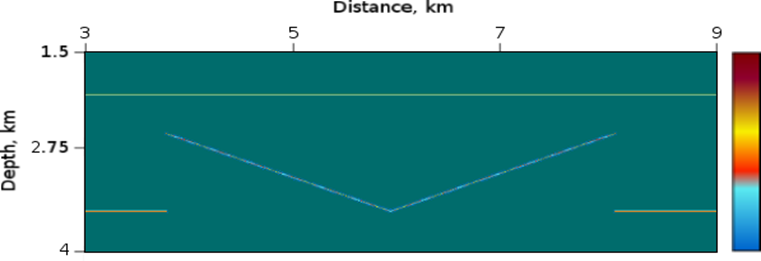
Figure 3: Thin slanted layers
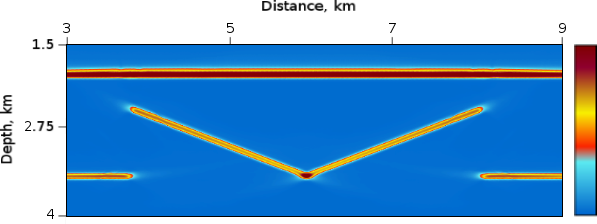
Figure 4: RTH Depth Migration Reflection
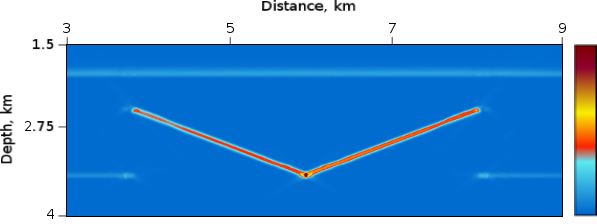
Figure 5: RTH Depth Migration Reflection. Only sloped layers detected
More detail:
Erokhin G., Pestov L., Danilin A., Kozlov M., and Ponomarenko D., 2017,
Interconnected vector pairs image conditions: New possibilities for visualization of acoustical media, 2017, SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2017: 4624-4629., https://doi.org/10.1190/segam2017-17587902.1
Two layers model
The velocity is 3 km/s in the upper media and 4 km/s in the down media.

Figure 1: Two layers model
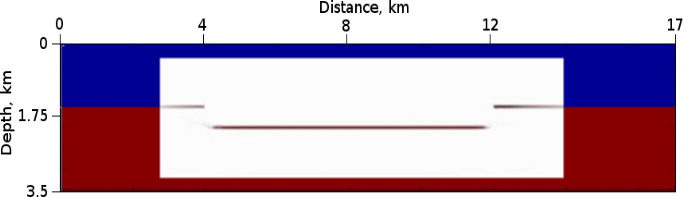
Figure 2: RTH Depth Migration Reflection
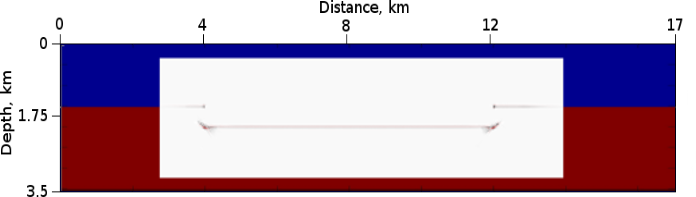
Figure 3: RTH Depth Migration Diffraction
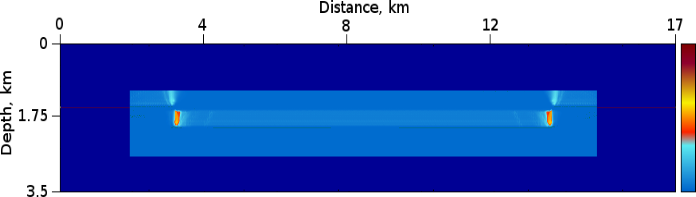
Figure 4: RTH Prism wave
Hard and soft diifractors model
The left diffractor has reduced velocity by 0.1 km/s w.r.t. background velocity 3.0 km/s , the right one has increased velocity by 0.1 km/s
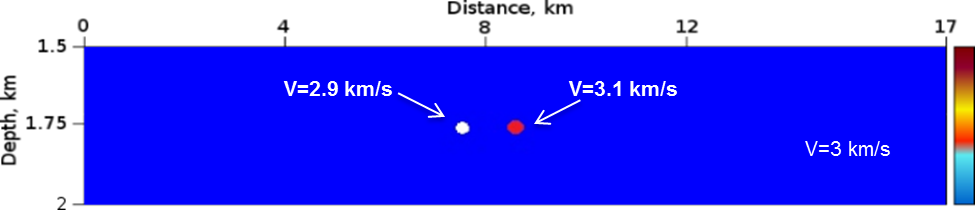
Figure 1 : Model of “soft” and “hard” diffractors
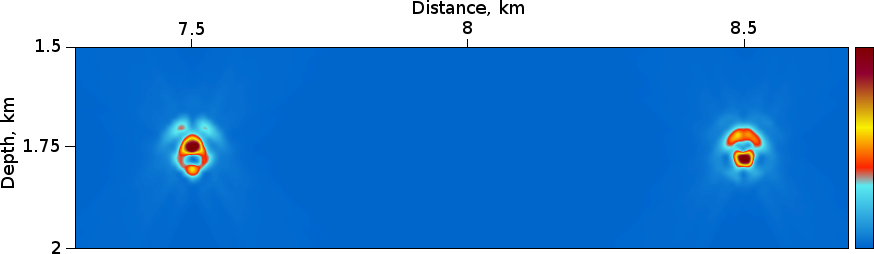
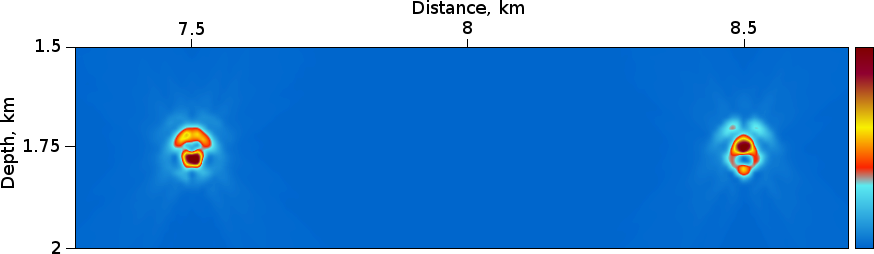
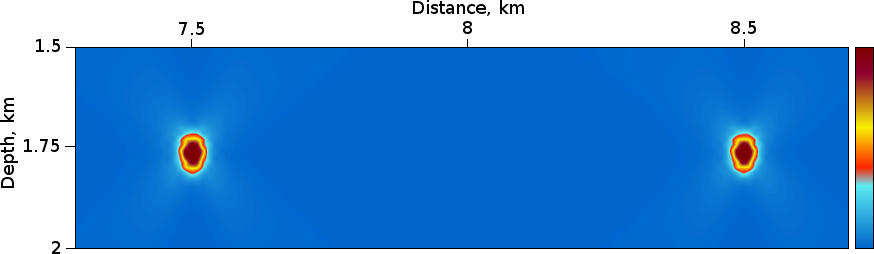
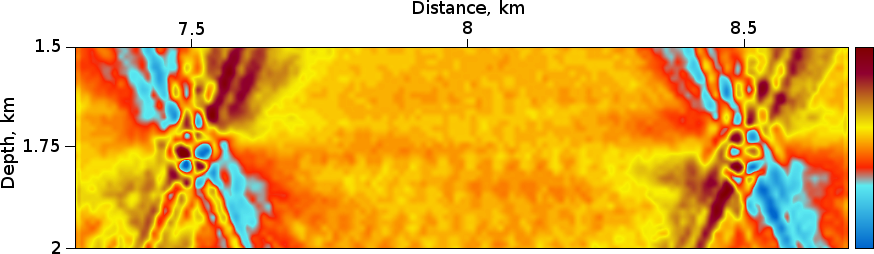
Figure 2 : RTH Depth Migration soft diffractor filter (a), hard diffractor filter (b), soft & hard diffractor filter (c), RTH Dip Angle Variance (d).
More detail:
Erokhin G., Pestov L., Danilin A., Kozlov M., and Ponomarenko D., 2017,
Interconnected vector pairs image conditions: New possibilities for visualization of acoustical media, 2017, SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2017: 4624-4629., https://doi.org/10.1190/segam2017-17587902.1
Marmousei2 model.
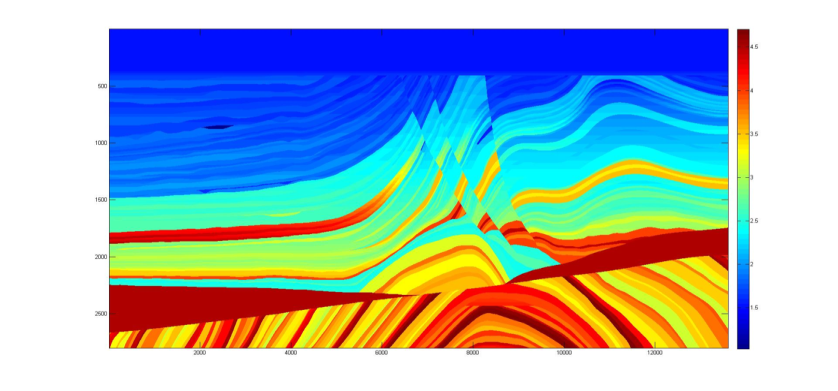
Figure 1: Marmousei2 model
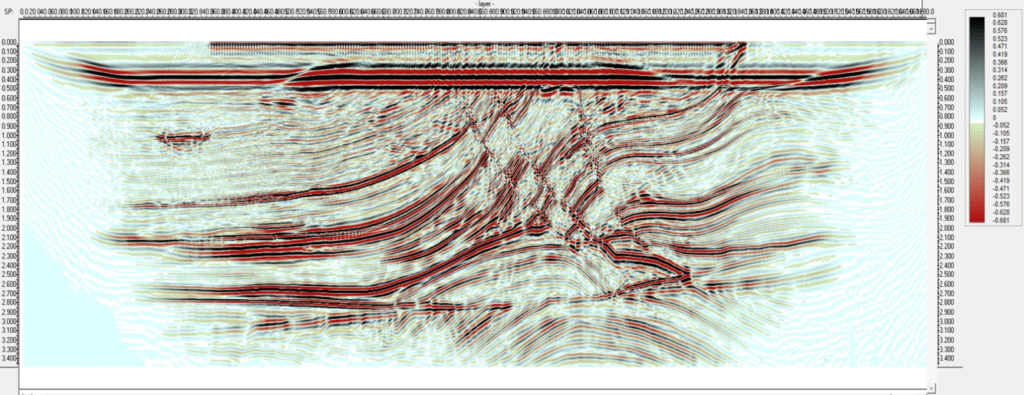
Figure 2: Conventional RTM
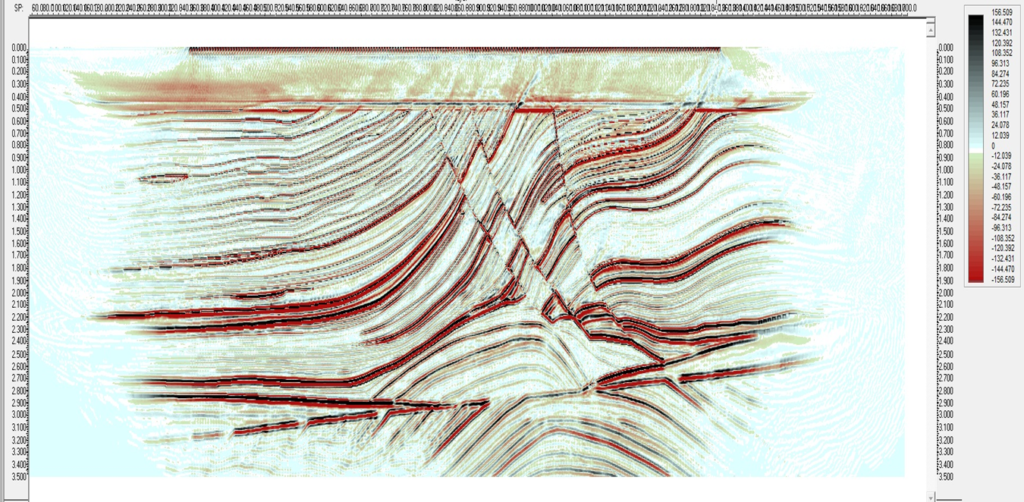
Figure 3: RTH Depth migration
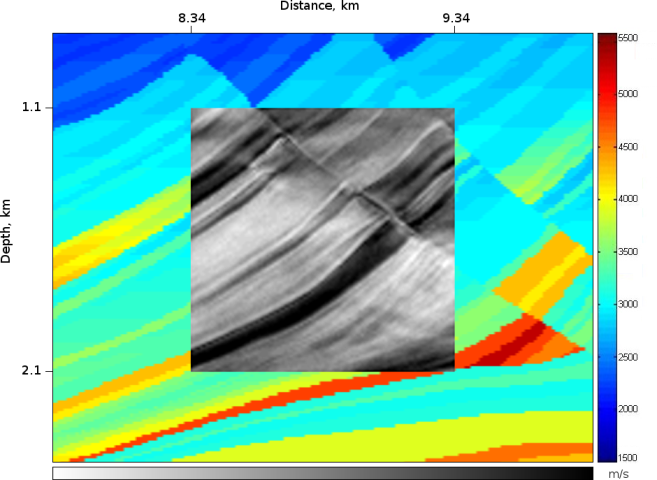
Figure 4: RTH Dip Angle Variance (part)
Gradient velocity model
Figure 1: The gradient initial velocity model
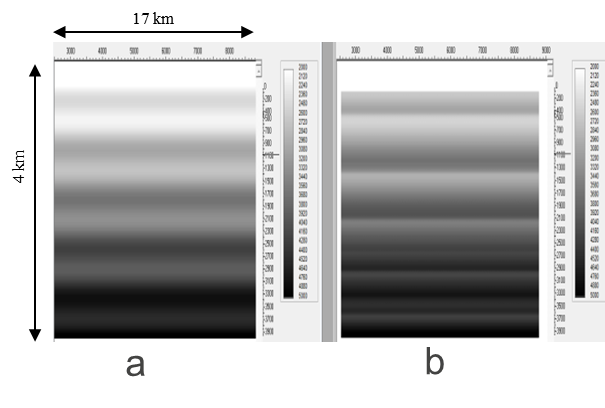
Figure 2: The true velocity (a), RTH velocity (b)
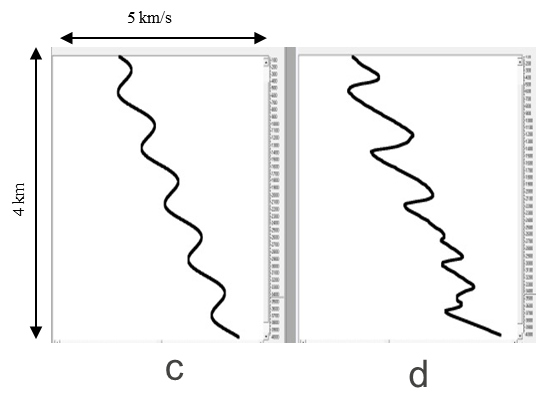
Figure 3: The true velocity profile (c), RTH velocity (d)